Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) represent a critical component of modern healthcare delivery, providing specialized surgical services in outpatient settings. As these facilities continue to expand their role in the healthcare ecosystem, the importance of robust credentialing processes cannot be overstated. ASC credentialing serves as the foundation for maintaining high standards of patient care, regulatory compliance, and operational excellence.
ASC Credentialing Essentials
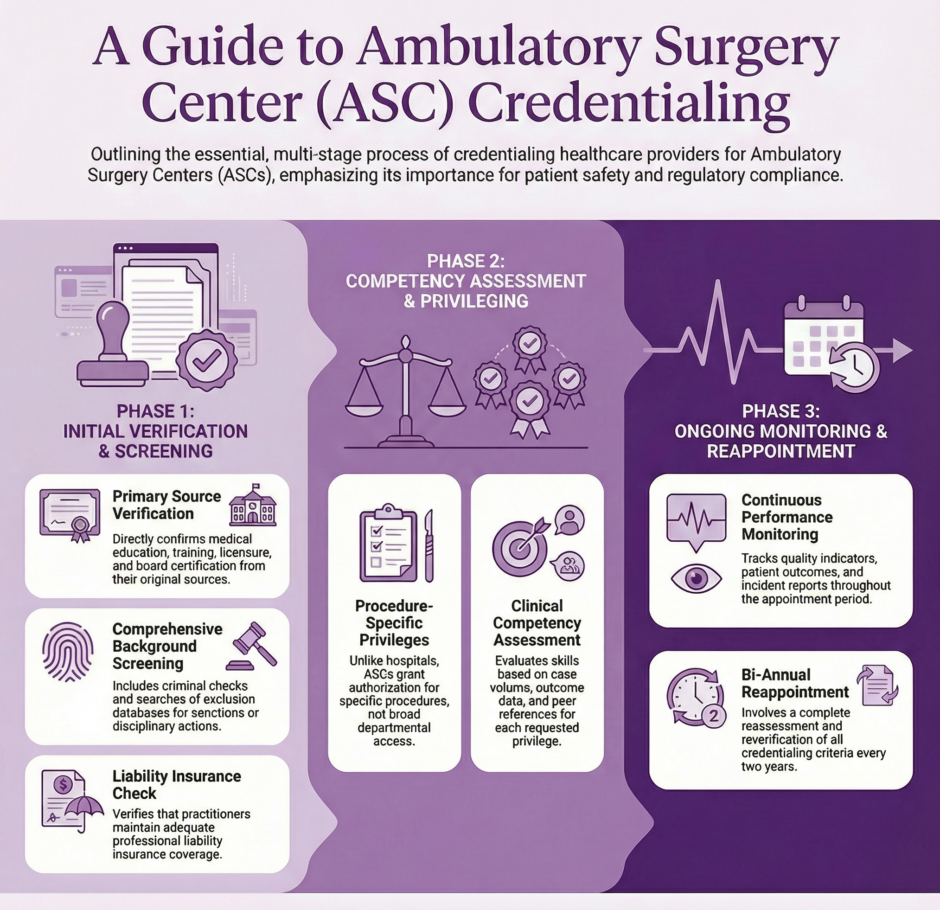
ASC credentialing is the systematic process through which ambulatory surgery centers verify and validate the qualifications, competencies, and professional standing of healthcare providers who seek privileges to practice within their facilities. This process extends beyond simple verification of licenses and certifications to include thorough evaluation of education, training, professional experience, and ongoing competency assessment.
The credentialing process in ASCs differs significantly from hospital-based credentialing due to the unique operational characteristics of ambulatory surgery centers. ASCs typically focus on specific surgical specialties and procedures, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise. This specialization demands that credentialing committees possess deep understanding of the specific requirements and standards applicable to their particular surgical focus areas.
What is ASC?
Regulatory Framework and Standards
The regulatory landscape governing ASC credentialing involves multiple layers of oversight and standards. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) establishes baseline requirements for ASCs participating in federal healthcare programs. These regulations mandate that ASCs maintain credentialing processes that ensure only qualified practitioners provide services to patients.
 State licensing boards provide another layer of regulatory oversight, with requirements varying significantly across jurisdictions. ASCs must navigate these state-specific requirements while maintaining compliance with federal standards. Additionally, accreditation organizations such as the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC), The Joint Commission, and the American Association for Accreditation of Ambulatory Surgery Facilities (AAAASF) establish additional standards that often exceed minimum regulatory requirements.
State licensing boards provide another layer of regulatory oversight, with requirements varying significantly across jurisdictions. ASCs must navigate these state-specific requirements while maintaining compliance with federal standards. Additionally, accreditation organizations such as the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC), The Joint Commission, and the American Association for Accreditation of Ambulatory Surgery Facilities (AAAASF) establish additional standards that often exceed minimum regulatory requirements.
Professional societies and specialty boards contribute to the credentialing framework by establishing practice standards, continuing education requirements, and competency assessments specific to their respective specialties. This multi-layered approach ensures that credentialing processes remain current with advancing medical knowledge and changing practice patterns.
Core Components of ASC Credentialing
The credentialing process typically begins with primary source verification of basic qualifications. This includes verification of medical school education, residency training, fellowship completion where applicable, and board certification status. ASCs must verify current licensure in all states where the practitioner holds licenses and confirm that no restrictions or disciplinary actions exist.
Professional liability insurance verification represents another critical component, ensuring that practitioners maintain adequate coverage limits consistent with ASC requirements and state regulations. This verification must include confirmation of coverage periods, exclusions, and any claims history that might impact practice privileges.
Competency assessment forms the cornerstone of effective credentialing programs. ASCs must establish clear criteria for evaluating clinical competency in the specific procedures and services offered within their facilities. This assessment often includes review of procedure-specific training, volume requirements, outcome data, and peer references from other facilities where the practitioner has provided similar services.
Background screening encompasses criminal background checks, exclusion database searches, and verification of any sanctions or disciplinary actions by licensing boards, hospitals, or other healthcare facilities. This screening process helps identify potential risks to patient safety and facility operations.
Privileging Process in ASCs
The privileging process in ASCs focuses on granting specific procedural authorizations rather than broad departmental privileges common in hospital settings. This procedure-specific approach requires detailed evaluation of training, experience, and competency for each requested privilege. ASCs must establish clear criteria for granting privileges, including minimum case volume requirements, specific training prerequisites, and outcome benchmarks.
 Temporary privileges may be granted in certain circumstances, allowing practitioners to provide services while full credentialing processes are completed. However, these temporary arrangements require careful oversight and clear limitations to ensure patient safety is not compromised. The duration and scope of temporary privileges must be clearly defined and regularly monitored.
Temporary privileges may be granted in certain circumstances, allowing practitioners to provide services while full credentialing processes are completed. However, these temporary arrangements require careful oversight and clear limitations to ensure patient safety is not compromised. The duration and scope of temporary privileges must be clearly defined and regularly monitored.
Privilege delineation becomes particularly important in ASCs due to their specialized nature. The credentialing committee must carefully consider the complexity of requested procedures, facility capabilities, emergency response protocols, and patient selection criteria when granting privileges. This careful consideration helps ensure that practitioners only perform procedures within their competency levels and that the facility can adequately support the requested services.
Ongoing Monitoring and Reappointment
ASC credentialing extends far beyond initial appointment to include ongoing monitoring of practitioner performance and periodic reappointment processes. Continuous monitoring systems track quality indicators, patient outcomes, incident reports, and peer feedback to identify potential performance issues or areas for improvement.
The reappointment process typically occurs every two years and involves reassessment of all credentialing criteria used during initial appointment. This includes reverification of licenses, certifications, insurance coverage, and background screening. Additionally, the reappointment process incorporates performance data collected during the previous appointment period, including quality metrics, patient satisfaction scores, and peer evaluations.
Professional development and continuing education requirements must be verified during reappointment to ensure practitioners maintain current knowledge and skills. ASCs may establish facility-specific continuing education requirements beyond those mandated by licensing boards or specialty organizations.
Technology and Credentialing Management
Modern ASC credentialing increasingly relies on technology solutions to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and reduce administrative burden. Credentialing management systems automate many routine verification tasks, track expiration dates, and maintain centralized databases of practitioner information.
Electronic primary source verification services reduce the time and effort required for initial credentialing while improving accuracy and reliability of verification processes. These services directly interface with licensing boards, educational institutions, and certification organizations to obtain verified information.
Digital document management systems facilitate secure storage and retrieval of credentialing files while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and accreditation standards. These systems often include automated alert functions that notify administrators of approaching expiration dates or required updates.
Quality Assurance and Risk Management
ASC credentialing serves as a primary risk management tool, helping facilities identify and mitigate potential risks associated with practitioner performance and patient safety. Effective credentialing processes help prevent incidents that could result in patient harm, liability exposure, or regulatory sanctions.
 Quality assurance programs integrated with credentialing processes provide ongoing assessment of practitioner performance and facility outcomes. These programs may include peer review activities, case discussions, and quality improvement initiatives designed to maintain and improve care standards.
Quality assurance programs integrated with credentialing processes provide ongoing assessment of practitioner performance and facility outcomes. These programs may include peer review activities, case discussions, and quality improvement initiatives designed to maintain and improve care standards.
The credentialing committee plays a crucial role in quality assurance by reviewing performance data, investigating incidents, and making recommendations for corrective action when necessary. This committee must maintain appropriate expertise in the specialties represented within the ASC while ensuring fair and objective evaluation processes.
Challenges and Best Practices
ASC credentialing faces several unique challenges that require careful attention and strategic planning. Limited administrative resources in many ASCs can make it difficult to maintain robust credentialing programs comparable to those found in larger healthcare organizations. This resource constraint requires efficient processes and may necessitate outsourcing certain credentialing functions to specialized organizations.
Practitioner mobility presents another challenge, as many ASC practitioners maintain privileges at multiple facilities and may frequently change practice locations. This mobility requires enhanced communication and coordination between facilities to ensure accurate and current information sharing.
Best practices for ASC credentialing include establishing clear policies and procedures, maintaining consistent application of standards, providing adequate training for credentialing staff, and regularly reviewing and updating credentialing criteria to reflect current practice standards and regulatory requirements.
Summary: The Future of ASC Credentialing
![]() The future of ASC credentialing will likely be shaped by technological advances, regulatory changes, and changing practice patterns within ambulatory surgery. Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies may eventually assist in risk assessment and performance monitoring, while blockchain technology could provide secure and immutable credentialing records.
The future of ASC credentialing will likely be shaped by technological advances, regulatory changes, and changing practice patterns within ambulatory surgery. Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies may eventually assist in risk assessment and performance monitoring, while blockchain technology could provide secure and immutable credentialing records.
Interstate licensing compacts and telemedicine expansion may influence credentialing requirements and processes, particularly for practitioners providing services across state lines. ASCs must remain adaptable to these changing requirements while maintaining rigorous standards for patient safety and quality care.
ASC credentialing remains an essential function that requires ongoing attention, resources, and expertise to ensure effective implementation.
Contact us to handle all of your ASC credentialing needs and/or challenges.

