Maintaining up-to-date medical credentials isn’t just a professional requirement, it’s a critical component of delivering high-quality patient care, ensuring patient safety, and protecting one’s professional standing. We’ll walk healthcare providers through the essential strategies, challenges, and best practices for keeping their credentials current and their professional knowledge sharp.
Understanding the Importance of Credential Maintenance
Credential maintenance or re-credentialing is far more than a bureaucratic checkbox.
It represents a healthcare provider’s commitment to:
- Professional Excellence: Credentials demonstrate a provider’s ongoing dedication to maintaining the highest standards of medical practice.
- Patient Safety: Up-to-date credentials ensure that healthcare professionals are knowledgeable about the latest medical techniques, technologies, and best practices.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions mandate ongoing education and credential renewal to practice legally.
- Professional Credibility: Current credentials signal to patients, employers, and colleagues that a healthcare provider is committed to continuous learning and improvement.
Key Credential Components for Healthcare Providers
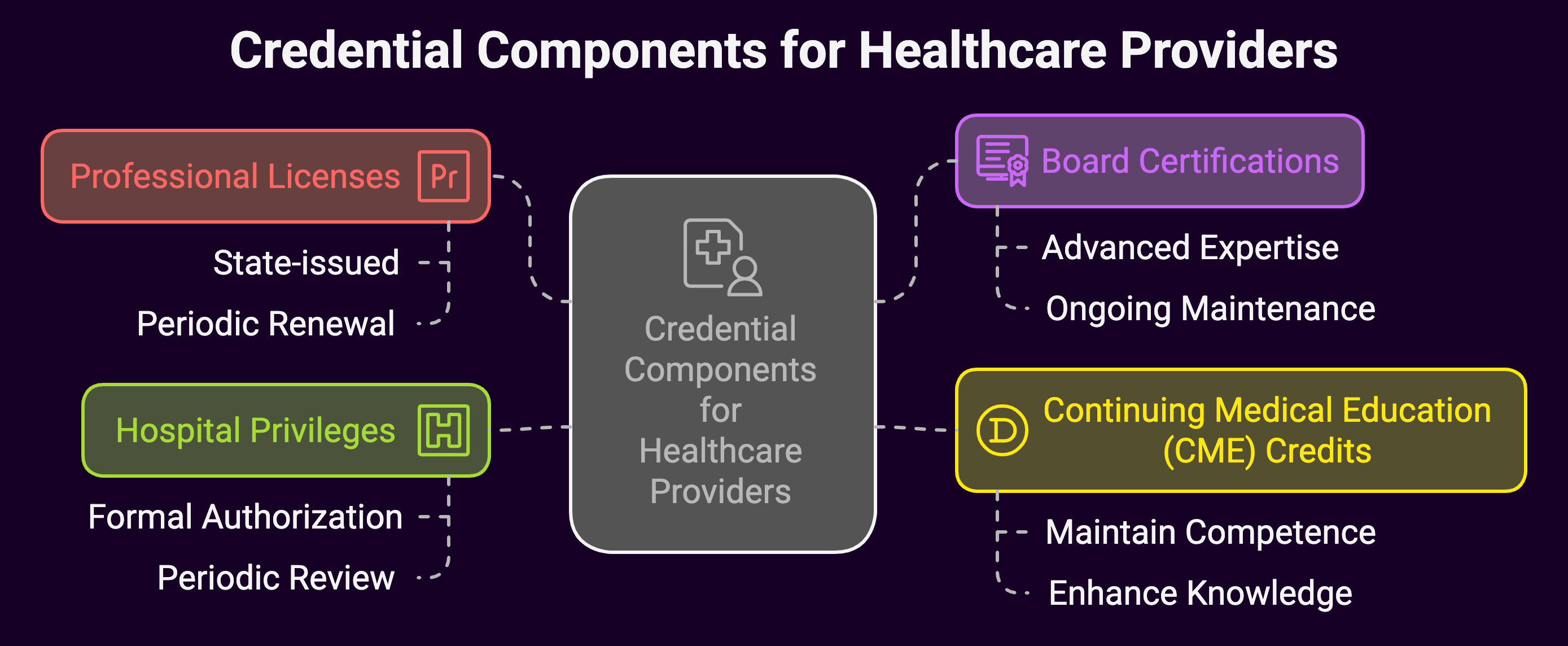
Before diving into maintenance strategies, it’s crucial to understand the primary credential components most healthcare professionals must manage:
 1. Professional Licenses
1. Professional Licenses
- State-issued licenses that authorize practice in a specific healthcare discipline
- Typically require periodic renewal with specific continuing education requirements
- Renewal periods and requirements vary by state and professional category
2. Board Certifications
- Specialized credentials demonstrating advanced expertise in a specific medical specialty
- Often require ongoing maintenance through:
- Periodic examination
- Continuous learning activities
- Performance assessment
- Demonstration of current medical knowledge
3. Continuing Medical Education (CME) Credits
- Structured learning experiences designed to maintain and enhance professional competence
- Critical for staying current with medical advances
- Requirements vary by specialty, state, and professional organization
4. Hospital Privileges
- Formal authorization to provide specific patient care services within a healthcare facility
- Require periodic review and renewal
- Dependent on maintaining active licenses, certifications, and professional standing
Developing a Comprehensive Credential Management Strategy
1. Create a Centralized Tracking System
Successful credential maintenance begins with robust organization.
Healthcare providers should:
- Develop a comprehensive digital or physical tracking system
- Maintain a master calendar of renewal dates
- Set up automated reminders at least 90 days before credential expiration
- Include critical information for each credential:
- Issued date
- Expiration date
- Renewal requirements
- Associated documentation
Recommended Tracking Tools
- Specialized credential management software
- Professional association management platforms
- Advanced spreadsheet systems with built-in alerts
- Mobile apps designed for healthcare professionals
2. Stay Informed About Changing Requirements
Healthcare regulations and professional standards are dynamic and evolve continuously.
Providers must:
- Subscribe to professional organization newsletters
- Follow state licensing board communications
- Attend annual professional conferences
- Join professional online forums and discussion groups
- Regularly review official websites of:
- State medical boards
- National professional associations
- Specialty certification boards
3. Systematic Continuing Education Planning
Proactive CME credit acquisition is essential.
Develop a strategic approach by:
- Mapping out annual educational goals
- Identifying relevant conferences, workshops, and online courses
- Diversifying learning modalities:
- In-person conferences
- Online webinars
- Peer-review journal readings
- Academic research participation
- Simulation-based training
CME Credit Acquisition Strategies
- Attend specialty-specific conferences
- Participate in professional webinars
- Engage in online learning platforms
- Complete self-assessment modules
- Publish research in peer-reviewed journals
- Participate in quality improvement projects
4. Digital Documentation Management
Modern credential maintenance requires sophisticated digital document management:
- Scan and digitize all critical credentials
- Maintain both physical and digital copies
- Use cloud storage with robust security
- Create backup copies in multiple secure locations
- Implement a systematic file naming convention
Recommended Digital Storage Practices
- Use HIPAA-compliant cloud storage services
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Regularly update and verify document accessibility
- Maintain a comprehensive inventory of stored documents
5. Financial Planning for Credential Maintenance
Credential maintenance involves significant financial investment.
Develop a strategic financial approach:
- Budget annually for:
- Examination fees
- License renewal costs
- CME course expenses
- Professional membership dues
- Explore employer reimbursement programs
- Consider professional tax deductions for educational expenses
- Investigate group discounts through professional associations
Technology’s Role in Credential Management
Digital Credential Verification Platforms
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing credential management:
- Blockchain-based verification systems
- Real-time credential validation networks
- AI-powered tracking and prediction tools
- Integrated professional profile platforms
Automation and AI Integration
Advanced platforms now offer:
- Automatic expiration alerts
- Personalized learning recommendations
- Predictive compliance forecasting
- Streamlined renewal processes
Common Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
1. Time Constraints
- Schedule dedicated time for credential management
- Break tasks into manageable monthly segments
- Leverage technology for efficiency
2. Financial Limitations
- Seek employer sponsorship
- Explore affordable online learning options
- Take advantage of group discounts
- Prioritize most critical credentials
3. Complex Regulatory Landscape
- Join professional mentorship programs
- Network with experienced colleagues
- Consult credential management specialists
- Attend professional development workshops
Special Considerations for Different Healthcare Specialties
Physicians
- More complex board certification requirements
- Frequent technological and procedural updates
- Higher stakes for credential maintenance
Nurses
- State-specific licensing nuances
- Multiple potential specialization tracks
- Emphasis on continuous skill development
Allied Health Professionals
- Diverse credential requirements
- Technology-driven skill evolution
- Increasing interdisciplinary collaboration needs
Legal and Ethical Implications
Consequences of Credential Lapses
- Potential loss of practice authorization
- Professional liability risks
- Reduced employment opportunities
- Potential legal repercussions
Ethical Responsibilities
- Transparent reporting of credentials
- Commitment to patient safety
- Continuous professional development
- Maintaining high ethical standards
Summary: A Proactive Approach to Professional Growth
Implementing a strategic, technology-enabled approach, allows healthcare providers to transform credential management from a bureaucratic burden into a powerful tool for continuous improvement.
Successful providers will be those who view credential maintenance not as a checkbox, but as an opportunity for ongoing learning, innovation, and enhanced patient care.
Additional Resources
- Professional Association Websites
- State Medical Board Portals
- Continuing Education Platforms
- Credential Management Software Directories
Note: Always consult specific state regulations and professional board requirements, as credential maintenance details can vary significantly by location and specialty.


 1. Professional Licenses
1. Professional Licenses