Few back-office processes have remained as stubbornly analog as provider credentialing. For years, healthcare administrators have wrestled with mountains of paperwork, endless phone calls, and frustratingly slow verification timelines that can stretch for months. Yet, here’s the good news: technology is finally disrupting this critical yet cumbersome process, bringing much-needed efficiency, accuracy, and transparency to credentialing.
 If you’ve ever been involved in credentialing healthcare providers, you know the pain points all too well. The repetitive data entry, the constant follow-ups with primary sources, the frantic searches for missing documents, and the pressure of knowing that until credentialing is complete, your organization can’t bill for a provider’s services.
If you’ve ever been involved in credentialing healthcare providers, you know the pain points all too well. The repetitive data entry, the constant follow-ups with primary sources, the frantic searches for missing documents, and the pressure of knowing that until credentialing is complete, your organization can’t bill for a provider’s services.
The Traditional Credentialing Process: A Recipe for Frustration
Before we jump into how technology is transforming credentialing, let’s take a moment to remember what the traditional process looks like and why it’s so ripe for disruption.
Provider credentialing has historically been a labor-intensive, manual process that involves collecting and verifying a vast array of information about healthcare providers.
This includes:
- Education and training history
- License verification
- Board certification
- Work history
- Malpractice insurance
- Hospital affiliations
- References
- Criminal background checks
- Sanction and exclusion checks
For each of these elements, credentialing specialists must request verification from primary sources, track responses, follow up on missing information, and update records accordingly. The process is further complicated by the fact that different payers and healthcare facilities may have different credentialing requirements, forcing providers to complete similar but slightly different applications numerous times.
Traditional Credentialing Pain Points
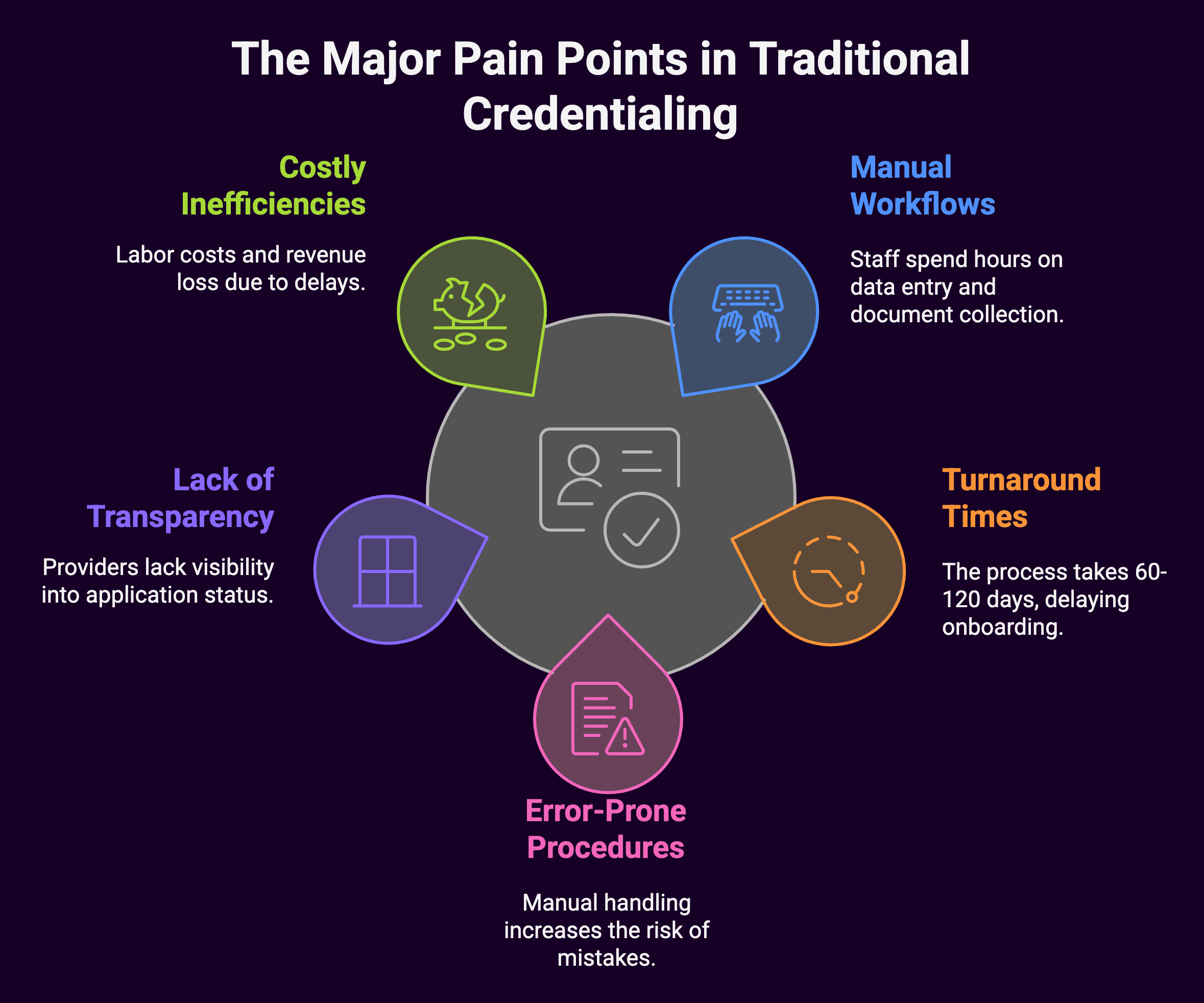
The traditional process suffers from several major pain points:
- Time-consuming manual workflows: Staff spend countless hours on data entry, document collection, and follow-up communications.
- Lengthy turnaround times: The average credentialing process takes 60-120 days from start to finish, delaying provider onboarding and billing.
- Error-prone procedures: Manual data entry and document handling increase the risk of mistakes that can further delay the process.
- Lack of transparency: Providers and administrators often lack visibility into where applications stand in the credentialing pipeline.
- Costly inefficiencies: The administrative burden of manual credentialing translates into significant labor costs and potential revenue loss due to delayed billing.
Now that we’ve set the stage, let’s explore how technology is addressing each of these pain points and transforming the credentialing landscape.
Cloud-Based Credentialing Platforms: The Digital Revolution Begins
The first major technological advancement in provider credentialing came with the introduction of cloud-based credentialing platforms. These comprehensive software solutions centralize the entire credentialing process, creating a single source of truth for provider data and documentation.
Key Features of Modern Credentialing Platforms
Today’s cloud-based credentialing platforms offer a wide range of features designed to streamline and automate the process:
- Digital application forms that eliminate paper and can be completed online by providers
- Document upload capabilities for licenses, certifications, and other required paperwork
- Centralized provider databases that store all credential information in one secure location
- Automated workflow management that tracks tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities
- Integrated primary source verification tools that initiate and track verification requests
- Real-time status tracking for applications as they move through the credentialing pipeline
- Reporting and analytics to identify bottlenecks and measure process efficiency
- Integration capabilities with other healthcare systems, including EHRs and billing platforms
The Benefits of Cloud-Based Credentialing
The shift to cloud-based platforms has delivered significant benefits to healthcare organizations:
- Reduced administrative burden: Digital platforms eliminate much of the manual work involved in credentialing, freeing staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
- Faster turnaround times: By automating routine tasks and streamlining workflows, cloud platforms can cut credentialing time by 50% or more.
- Improved accuracy: Digital validation tools catch errors and inconsistencies early in the process, reducing delays caused by incorrect information.
- Enhanced transparency: Providers and administrators can track application status in real-time, eliminating uncertainty and reducing status update calls.
- Better resource allocation: With automation handling routine tasks, credentialing specialists can focus on complex cases and relationship management.
Automated Primary Source Verification: The End of Phone Tag
One of the most time-consuming aspects of traditional credentialing is primary source verification (PSV), the process of contacting each institution, licensing board, or organization directly to verify a provider’s credentials. This process has historically involved countless phone calls, faxes, emails, and follow-ups, often stretching over weeks or months.
Technology has transformed this aspect of credentialing through automated PSV solutions that connect directly with primary sources, drastically reducing verification times and eliminating the need for manual outreach in many cases.
How Automated PSV Works
Modern automated PSV systems operate through several technological mechanisms:
- Direct API integrations with licensing boards, medical schools, certification bodies, and other primary sources that allow for real-time data verification
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) that can navigate websites, complete verification forms, and extract information much like a human would, but at machine speed
- Continuous monitoring services that automatically check for license expirations, sanctions, exclusions, and other status changes that might affect a provider’s credentials
- Digital credential passports that store verified information in a secure, portable format that can be shared across organizations
The Impact of Automated PSV
The benefits of automated primary source verification include:
- Dramatic time savings: Verifications that once took weeks can now be completed in minutes or hours
- Higher accuracy rates: Eliminating manual data entry reduces transcription errors and other mistakes
- Continuous compliance: Automated monitoring ensures organizations are immediately notified of any credential issues
- Reduced workforce requirements: Less manual verification work means teams can handle higher volumes with the same staffing levels
- Improved provider experience: Faster verification means providers can start practicing—and billing—sooner
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The Smart Credentialing Revolution
While cloud platforms and automated PSV have dramatically improved the credentialing process, the latest wave of innovation comes from artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are bringing unprecedented levels of intelligence and efficiency to provider credentialing.
AI Applications in Credentialing
AI and ML are being applied to credentialing in several powerful ways:
- Intelligent document processing: AI-powered systems can “read” scanned documents, extract relevant information, and populate database fields automatically. This eliminates the need for manual data entry from paper documents or PDFs.
- Predictive analytics: ML algorithms can analyze historical credentialing data to predict which applications are likely to face delays or complications, allowing staff to proactively address potential issues.
- Natural language processing: AI systems can interpret and respond to email inquiries, generate verification requests, and even communicate with providers about missing information.
- Anomaly detection: ML models can identify unusual patterns or inconsistencies in provider applications that might indicate potential issues requiring human review.
- Intelligent workflow routing: AI can automatically prioritize and route tasks based on complexity, urgency, and staff workload to optimize resource allocation.
Real-World Impact of AI in Credentialing
Organizations that have implemented AI-powered credentialing solutions report significant benefits:
- Up to 80% reduction in manual data entry through intelligent document processing
- 30-40% improvement in first-pass accuracy rates for applications
- Ability to predict potential credentialing delays with 85%+ accuracy
- 50% reduction in routine email communications through automated responses and updates
- More equitable staff workload distribution through intelligent task routing
Blockchain Technology: The Future of Credential Verification
Perhaps the most revolutionary technology beginning to impact provider credentialing is blockchain. While still in the early stages of adoption in healthcare, blockchain has the potential to fundamentally transform how credentials are verified, stored, and shared.
How Blockchain Works for Credentialing
Blockchain technology creates a distributed, immutable ledger of verified credentials that can be securely shared across organizations.
Here’s how it applies to provider credentialing:
- Verified once, used many times: When a credential is verified by a trusted entity (like a medical school or licensing board), that verification is recorded on the blockchain and becomes permanently available to any authorized party.
- Self-sovereign identity: Providers maintain control over their credential information while being able to share verified data instantly with hospitals, insurance companies, and other stakeholders.
- Smart contracts: Automated verification processes can be encoded as smart contracts on the blockchain, eliminating the need for manual verification entirely.
- Immutable audit trail: Every verification, update, and access to credential information is permanently recorded, creating an unalterable history.
The Blockchain Advantage
Though still emerging, blockchain-based credentialing solutions offer several compelling advantages:
- Elimination of redundant verifications: Once a credential is verified on the blockchain, it never needs to be re-verified by another organization.
- Near-instant credential sharing: Providers can grant immediate access to their verified credentials to any new organization.
- Reduction in fraud: The immutable nature of blockchain makes credential falsification extremely difficult.
- Decreased dependency on intermediaries: Direct verification reduces the need for third-party verification services.
- Global credential portability: Blockchain can facilitate credential recognition across institutional and geographic boundaries.
Mobile Technology: Credentialing in the Palm of Your Hand
Another technological advancement transforming provider credentialing is the rise of mobile applications and responsive web platforms that allow providers to manage their credentialing process from anywhere, at any time.
Mobile Credentialing Features
Today’s mobile credentialing solutions offer providers a range of capabilities:
- Application submission and tracking from mobile devices
- Document capture using smartphone cameras
- Push notifications for application status updates and required actions
- Secure messaging with credentialing staff
- Digital signature capability for forms and attestations
- Credential wallet functionality to store and share digital credentials
The Mobile Advantage
Mobile technology brings several specific benefits to the credentialing process:
- Improved provider engagement: When providers can easily check status and respond to requests from their phones, they tend to be more responsive and engaged in the process.
- Faster document submission: The ability to snap a photo of a document and upload it instantly eliminates delays associated with scanning, faxing, or mailing paperwork.
- Reduced follow-up requirements: Push notifications eliminate the need for phone calls and emails to remind providers about missing information.
- Better provider experience: The convenience of mobile access contributes to higher provider satisfaction with the credentialing process.
- Location independence: Providers traveling between facilities or working in remote locations can still participate actively in the credentialing process.
Data Standardization and Interoperability: Breaking Down Silos
One of the most significant challenges in traditional credentialing has been the lack of standardization in data collection and the resulting inability to share information efficiently between organizations. Technology is addressing this issue through data standardization initiatives and interoperability solutions.
Key Standardization Developments
Several important developments are driving standardization in credentialing:
- CAQH ProView: This industry alliance has created a standardized provider data collection system used by over 1.4 million providers and most major health plans, allowing providers to enter information once for use by multiple organizations.
- HL7 FHIR standards: The Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources standard includes specifications for provider directory information, creating a common language for sharing credentialing data between systems.
- DirectTrust framework: This network enables secure, interoperable exchange of provider information between trusted entities.
- Digital provider directories: Centralized, digital directories maintain up-to-date provider information that can be accessed by multiple stakeholders.
The Benefits of Standardization and Interoperability
These standardization efforts deliver several important benefits:
- Reduced duplicate data entry for providers who can “enter once, use many times”
- Improved data accuracy through consistent formatting and validation rules
- Faster data exchange between credentialing systems, EHRs, and payer platforms
- Reduced provider burden by eliminating redundant information requests
- More complete provider profiles through the aggregation of data from multiple sources
Analytics and Business Intelligence: Data-Driven Credentialing
As credentialing has become more digital, organizations have gained access to rich data about their processes. Advanced analytics and business intelligence tools are helping them turn this data into actionable insights that drive continuous improvement.
Key Analytics Applications
Modern credentialing analytics focus on several key areas:
- Process efficiency metrics that track turnaround times, bottlenecks, and resource utilization
- Predictive models that forecast credentialing volumes and resource requirements
- Benchmarking tools that compare performance against industry standards and peer organizations
- ROI calculations that quantify the financial impact of credentialing improvements
- Provider satisfaction measurement that tracks the provider experience throughout the credentialing journey
The Analytics Advantage
Organizations using advanced analytics in their credentialing processes report several benefits:
- Data-driven process improvements based on identified bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- More accurate resource planning through volume forecasting and workload analysis
- Ability to set and track performance goals with real-time monitoring of key metrics
- Improved financial performance through faster onboarding and billing initiation
- Higher provider satisfaction through targeted improvements to pain points
Telehealth and Virtual Care: New Credentialing Challenges and Solutions
The explosive growth of telehealth and virtual care, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has created new challenges and opportunities in provider credentialing. Technology is helping organizations adapt to these new realities.
Telehealth Credentialing Innovations
Several technological innovations are specifically addressing telehealth credentialing needs:
- Interstate licensure verification tools that help manage the complexity of multi-state practice
- Telehealth-specific privileging modules that address the unique requirements of virtual care
- Digital identity verification systems that use biometrics and other tools to verify provider identity remotely
- Specialty telehealth credentialing platforms designed specifically for virtual care organizations
- Integration with telehealth platforms to ensure seamless provider onboarding
Meeting the Telehealth Challenge
These technologies are helping organizations address the unique aspects of telehealth credentialing:
- Managing interstate practice requirements as providers deliver care across state lines
- Accelerating privileging for crisis response when rapid provider deployment is needed
- Ensuring appropriate telehealth training verification for virtual care delivery
- Maintaining compliance with evolving telehealth regulations across multiple jurisdictions
- Handling higher volumes of credentials as organizations rapidly expand telehealth services
The Human Element: Technology as Enabler, Not Replacement
With all the technological advances in credentialing, it’s important to note that technology is enhancing rather than replacing the human element in the process. The most successful implementations combine powerful technology with skilled credentialing professionals.
The Evolving Role of Credentialing Specialists
As technology automates routine tasks, the role of credentialing specialists is evolving in several ways:
- Shift from data entry to data analysis as specialists focus on interpreting information rather than collecting it
- Greater emphasis on exception handling for complex cases that require human judgment
- More time for provider relationship management as administrative tasks are automated
- Development of technology expertise alongside traditional credentialing knowledge
- Focus on process improvement rather than process execution
The Technology-Human Partnership
The most effective credentialing functions leverage both technology and human expertise:
- Technology handles high-volume, routine verification tasks with speed and accuracy
- Humans manage complex edge cases that require judgment and investigation
- Technology provides data-driven insights to inform decision-making
- Humans build relationships with providers and stakeholders to facilitate collaboration
- Technology ensures consistent application of policies and standards
- Humans develop innovative solutions to emerging challenges
Implementation Challenges: Navigating the Technology Transition
While the benefits of technology-enabled credentialing are clear, organizations often face challenges in implementing new systems and approaches. Successful implementation requires careful planning and change management.
Common Implementation Challenges
Organizations typically encounter several challenges when implementing new credentialing technology:
- Data migration complexity when transferring information from legacy systems
- Integration difficulties with existing EHR, HR, and billing systems
- Staff resistance to change and new workflows
- Provider adoption hurdles for self-service features
- Budget constraints for technology investment
- Process redesign requirements to fully leverage new capabilities
Strategies for Successful Implementation
Organizations that successfully implement new credentialing technology typically follow several best practices:
- Phased implementation approaches that break the transition into manageable steps
- Comprehensive staff training programs that build confidence and proficiency
- Clear communication with providers about new processes and expectations
- Executive sponsorship to ensure organizational support and resource allocation
- Process optimization before automation to avoid digitizing broken workflows
- Regular feedback collection and response to address concerns quickly
- Celebration of early wins to build momentum and engagement
Return on Investment: The Business Case for Credentialing Technology
While the operational benefits of credentialing technology are compelling, healthcare leaders often need to see a clear return on investment to justify technology expenditures. Fortunately, the business case for credentialing technology is strong and quantifiable.
Calculating Credentialing ROI
Organizations can measure the return on credentialing technology investment in several ways:
- Reduced labor costs through automation of routine tasks
- Earlier billing initiation due to faster credentialing turnaround times
- Decreased provider vacancy costs through accelerated onboarding
- Reduced compliance risks and penalties through more accurate verification
- Lower recruiting costs due to improved provider experience and satisfaction
- Decreased opportunity costs as staff focus on higher-value activities
The Numbers Behind the ROI
The financial impact of credentialing technology can be substantial:
- Average revenue impact of credentialing delays: $7,500 – $30,000 per provider per month in lost billing
- Labor cost savings: 30-50% reduction in administrative hours per application
- Accelerated time to billing: 15-45 days earlier revenue capture per provider
- Compliance risk reduction: Potential savings of $10,000+ per incident in audit findings and remediation costs
- Provider satisfaction impact: 10-15% improvement in provider retention rates
The Future of Credentialing Technology: What’s Next?
As impressive as current credentialing technology is, the field continues to evolve rapidly. Several emerging trends point to even more transformative changes in the coming years.
Emerging Trends to Watch
The next wave of credentialing innovation is likely to include:
- Decentralized credential verification networks using blockchain that eliminate the need for repetitive verification entirely
- AI-powered credentialing assistants that can handle complex verification tasks and provider interactions
- Biometric verification systems that use facial recognition and other tools to confirm provider identity with absolute certainty
- Global credential passports that facilitate provider mobility across national boundaries
- Quantum-resistant security protocols to protect sensitive credentialing data against future threats
- Unified digital identity systems that merge clinical, financial, and administrative credentials
- Real-time credential monitoring that continuously verifies provider status rather than at periodic intervals
Preparing for the Future
Organizations can prepare for these emerging trends by:
- Establishing digital-first credentialing processes now to build the foundation for future advances
- Developing data governance frameworks that will support more sophisticated data sharing
- Investing in staff development to build skills for the next generation of credentialing technology
- Participating in industry standardization efforts to shape future direction
- Monitoring emerging technologies and pilot programs for potential adoption
- Building flexible technology architecture that can incorporate new capabilities as they emerge
Summary: Embracing the Credentialing Technology Revolution
Provider credentialing has long been a pain point for healthcare organizations. A necessary but burdensome process that consumes significant resources while delaying provider onboarding and revenue generation. Technology is finally changing this equation, transforming credentialing from an administrative burden into a strategic advantage.
From cloud-based platforms and automated verification to AI-powered analytics and blockchain solutions, technology is making credentialing faster, more accurate, and more efficient at every step. Organizations that embrace these innovations are seeing dramatic improvements in turnaround times, staff productivity, provider satisfaction, and financial performance.

