Data isn’t just information. It’s the lifeblood that powers every aspect of patient care, operational efficiency, and strategic decision-making. Healthcare Provider Data Management (HPDM) represents the systematic approach to collecting, storing, organizing, protecting, and utilizing the vast amounts of data that flow through healthcare organizations daily. From electronic health records to billing information, from clinical research data to patient satisfaction surveys, managing this information effectively can mean the difference between thriving in the modern healthcare environment and struggling to keep pace.
 Healthcare data management has manifested itself far beyond simple record-keeping. It’s become a sophisticated discipline that combines technology, governance, security, and analytics to transform raw information into actionable insights that improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and drive innovation. For healthcare providers negotiating an increasingly complex regulatory environment while trying to deliver exceptional patient care, understanding and implementing robust data management practices isn’t optional, it’s essential.
Healthcare data management has manifested itself far beyond simple record-keeping. It’s become a sophisticated discipline that combines technology, governance, security, and analytics to transform raw information into actionable insights that improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and drive innovation. For healthcare providers negotiating an increasingly complex regulatory environment while trying to deliver exceptional patient care, understanding and implementing robust data management practices isn’t optional, it’s essential.
Understanding the Scope of Healthcare Data
Healthcare organizations generate and handle an extraordinary variety of data types, each with its own unique characteristics, requirements, and challenges. Clinical data forms the core of most healthcare operations, encompassing everything from patient demographics and medical histories to diagnostic test results, treatment plans, and medication records. This information must be accurate, accessible, and secure, as it directly impacts patient safety and care quality.
Administrative data represents another crucial category, including insurance information, billing records, appointment scheduling, and facility management data. While this information might seem less critical than clinical data, it’s actually the backbone that keeps healthcare organizations financially viable and operationally efficient. Poor management of administrative data can lead to billing errors, compliance violations, and significant revenue loss.
Research and analytics data has become increasingly important as healthcare organizations embrace evidence-based medicine and population health management. This includes clinical trial data, outcome measurements, quality metrics, and comparative effectiveness research. The ability to analyze this information effectively can lead to breakthrough discoveries, improved treatment protocols, and better resource allocation.
Patient-generated data represents a rapidly growing category that includes information from wearable devices, mobile health apps, patient portals, and remote monitoring systems. As patients become more engaged in their healthcare and technology becomes more sophisticated, this data stream provides valuable insights into patient behavior, treatment adherence, and health outcomes outside traditional clinical settings.
The Technology Infrastructure Behind Data Management
Modern healthcare data management relies on sophisticated technology infrastructure that must balance accessibility, security, performance, and scalability. Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems serve as the central repository for most clinical information, but they’re just one component of a larger ecosystem that includes laboratory information systems, radiology systems, pharmacy management platforms, and countless other specialized applications.
Cloud computing has revolutionized healthcare data management by providing scalable storage solutions, advanced analytics capabilities, and improved disaster recovery options. Cloud platforms allow healthcare organizations to handle massive data volumes without investing in expensive on-premises infrastructure, while also enabling better collaboration and data sharing between different facilities and providers.
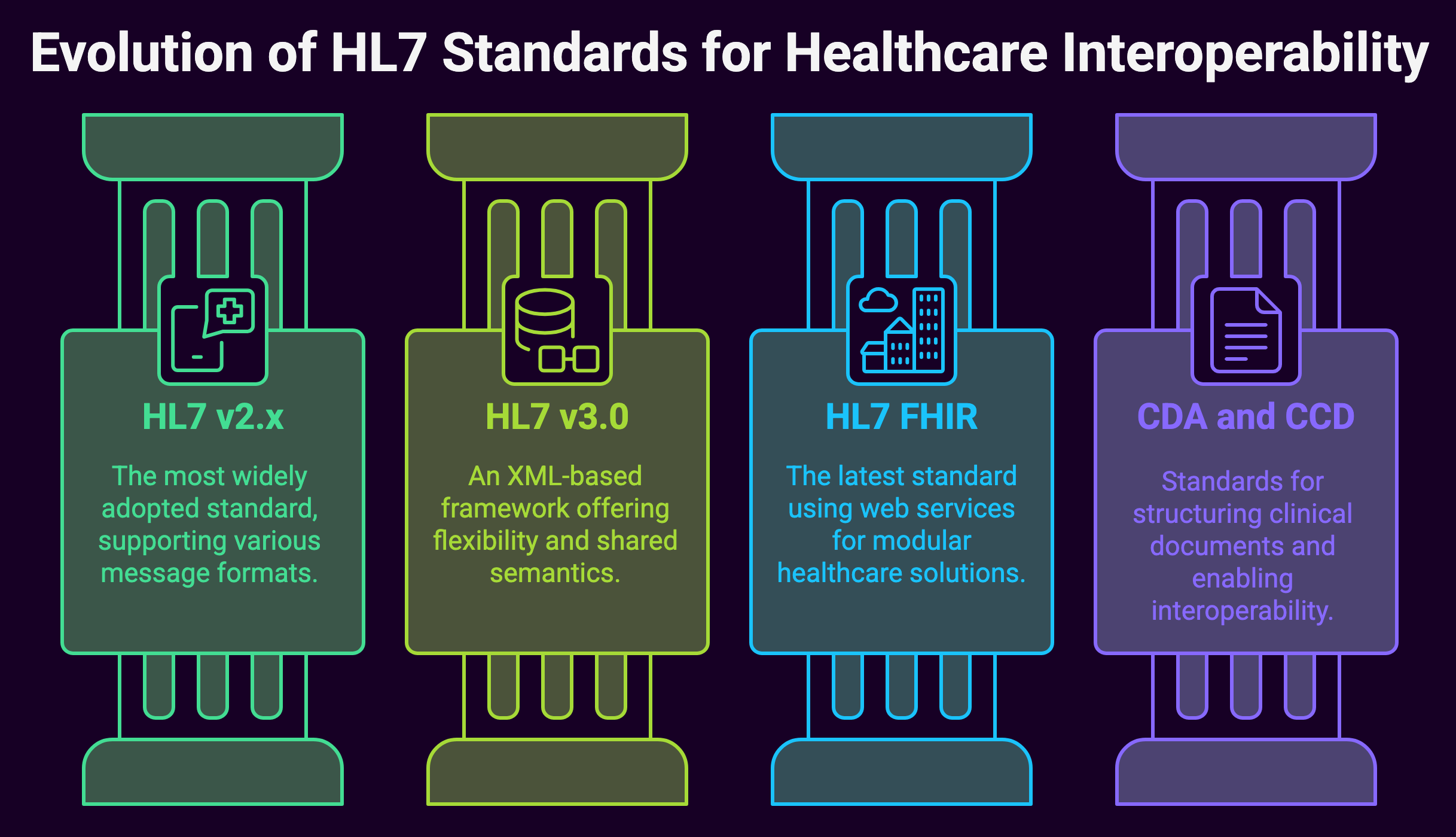
Interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) have become crucial for ensuring that different systems can communicate effectively. These standards enable seamless data exchange between various healthcare applications, reducing data silos and improving care coordination. When systems can share information seamlessly, healthcare providers can access complete patient information regardless of where the care was originally provided.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are increasingly integrated into healthcare data management platforms, providing capabilities for automated data analysis, predictive modeling, and clinical decision support. These technologies can identify patterns in large datasets that would be impossible for humans to detect, leading to earlier disease detection, more personalized treatment plans, and improved operational efficiency.
Data Governance and Quality Management
Effective healthcare data management requires robust governance frameworks that establish clear policies, procedures, and accountability structures for data handling. Data governance in healthcare involves defining who has access to what information, how data quality is maintained, what security measures are in place, and how data lifecycle management is handled.

Data quality management is particularly critical in healthcare settings where inaccurate information can have serious consequences for patient safety. This involves implementing validation rules, conducting regular data audits, establishing data cleansing procedures, and creating feedback loops to continuously improve data accuracy. Healthcare organizations must also address issues like duplicate records, incomplete information, and data inconsistencies that can compromise the integrity of their information systems.
Master data management (MDM) has become essential for healthcare organizations operating multiple facilities or systems. MDM ensures that critical information like patient identities, provider credentials, and facility details are consistent and accurate across all systems. This prevents issues like duplicate patient records, billing errors, and care coordination problems that can arise when the same information is stored differently in multiple systems.
Data stewardship programs assign specific individuals or teams responsibility for maintaining data quality within their areas of expertise. Clinical data stewards might focus on ensuring that diagnostic codes are accurate and complete, while administrative data stewards might concentrate on billing and insurance information. This distributed approach to data quality management helps ensure that subject matter experts are involved in maintaining the accuracy of specialized data types.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Healthcare data security represents one of the most challenging aspects of data management, given the sensitive nature of medical information and the strict regulatory requirements that govern its protection. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes minimum standards for protecting patient health information, but healthcare organizations must often go beyond these requirements to ensure encompassing security.
Cybersecurity threats targeting healthcare organizations have increased dramatically in recent years, with ransomware attacks, data breaches, and other security incidents becoming increasingly common. Healthcare data management systems must incorporate multiple layers of security, including encryption, access controls, network security, and continuous monitoring to protect against these threats.
Identity and access management systems ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific types of healthcare information. Role-based access controls limit data access based on job responsibilities, while audit logging tracks who accessed what information and when. These systems must balance security requirements with the need for healthcare providers to access patient information quickly during emergencies or urgent care situations.
Data privacy extends beyond security to include considerations about how patient information is used, shared, and retained. Healthcare organizations must establish clear policies about data sharing with third parties, research use of patient information, and patient rights regarding their own data. Privacy by design principles should be incorporated into all data management systems and processes.
Analytics and Business Intelligence
 Healthcare analytics has become a crucial component of data management, transforming raw information into actionable insights that can improve patient care, operational efficiency, and financial performance. Clinical analytics can identify patterns in patient outcomes, treatment effectiveness, and disease progression that inform evidence-based care decisions.
Healthcare analytics has become a crucial component of data management, transforming raw information into actionable insights that can improve patient care, operational efficiency, and financial performance. Clinical analytics can identify patterns in patient outcomes, treatment effectiveness, and disease progression that inform evidence-based care decisions.
Population health management relies heavily on data analytics to identify high-risk patient groups, track health trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of preventive care programs. By analyzing large datasets, healthcare organizations can identify patients who might benefit from specific interventions, allocate resources more effectively, and improve overall community health outcomes.
Financial analytics help healthcare organizations optimize revenue cycle management, identify cost reduction opportunities, and improve operational efficiency. This includes analyzing billing patterns, identifying denied claims, tracking key performance indicators, and forecasting financial performance.
Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future events, such as patient readmissions, equipment failures, or staffing needs. These insights enable healthcare organizations to be proactive rather than reactive, potentially preventing adverse events and optimizing resource allocation.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Healthcare data management must negotiate a tough regulatory landscape that includes federal laws like HIPAA and the HITECH Act, state regulations, and industry standards. Compliance requirements affect every aspect of data handling, from initial collection and storage to sharing and disposal.
Documentation and audit trails are essential for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements. Healthcare organizations must maintain detailed records of data access, modifications, and sharing activities. This documentation not only supports compliance efforts but also helps identify potential security issues or policy violations.
Risk assessment and management processes help healthcare organizations identify potential vulnerabilities in their data management systems and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. This includes evaluating risks related to data breaches, system failures, natural disasters, and other events that could compromise data integrity or availability.
Business continuity and disaster recovery planning ensure that healthcare organizations can continue operating and maintain access to critical patient information even during system outages or other disruptions. This requires robust backup systems, redundant infrastructure, and detailed recovery procedures that can be implemented quickly when needed.
The Future of Healthcare Data Management
Healthcare data management continues to change rapidly as new technologies, regulations, and care delivery models emerge. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will play increasingly important roles in automating data management tasks, improving data quality, and generating insights from complex datasets.
Interoperability will continue to improve as industry standards mature and healthcare organizations recognize the benefits of seamless data sharing. Patient-controlled data sharing models may give individuals more control over how their health information is used and shared.
Cloud computing adoption will accelerate as healthcare organizations seek to reduce infrastructure costs and improve scalability. Edge computing may become important for processing data from IoT devices and supporting real-time analytics in clinical settings.
Blockchain technology shows promise for improving data security, enabling secure data sharing, and creating immutable audit trails for critical healthcare information.
Summary: Healthcare Provider Data Management Efficacy
 Provider Data Management represents far more than simple information storage and retrieval. It’s a distinct discipline that combines technology, governance, security, and analytics to transform healthcare data into a strategic asset that improves patient care, enhances operational efficiency, and drives innovation.
Provider Data Management represents far more than simple information storage and retrieval. It’s a distinct discipline that combines technology, governance, security, and analytics to transform healthcare data into a strategic asset that improves patient care, enhances operational efficiency, and drives innovation.
Success in healthcare data management requires a holistic approach that addresses technical infrastructure, data governance, security and privacy, regulatory compliance, and analytics capabilities. Organizations that invest in robust data management capabilities position themselves to thrive in an increasingly data-driven healthcare environment, while those that neglect these foundational elements risk falling behind in quality, efficiency, and competitiveness.
With healthcare continuing to move toward value-based care, population health management, and personalized medicine, the importance of effective data management will only continue to grow. Healthcare organizations that recognize data management as a strategic priority and invest accordingly will be best positioned to succeed in the future of healthcare delivery.